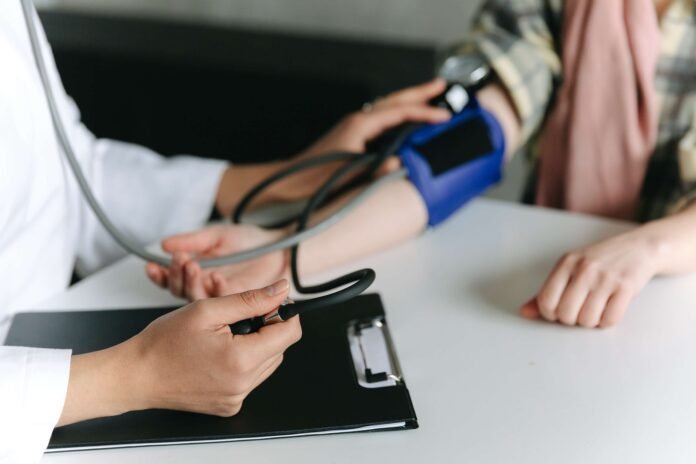
Introduction
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood flowing through your arteries is consistently too high, causing damage to your blood vessels and increasing your risk of serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Symptoms of high blood pressure can be difficult to detect because they often do not present any visible signs. However, some people may experience headaches, dizziness, or nosebleeds. In most cases, though, high blood pressure is usually discovered during routine check-ups with a healthcare professional.
Prevention is key when it comes to managing high blood pressure. Making lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can all help reduce the risk of developing this condition. If you have been told you have high blood pressure, you may also be given medicine along with changes to your lifestyle to help control your condition and keep it from getting worse.
Definition of High Blood Pressure (HBP)
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition where the force of blood against the walls of arteries is too high. When left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. Blood pressure readings are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and typically consist of two numbers: systolic (the top number) and diastolic (the bottom number). A healthy blood pressure reading is usually between 120 and 80 mmHg.
Having high blood pressure often presents no symptoms, which can make it difficult to detect without regular check-ups. However, some people may experience symptoms such as headaches, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds. High blood pressure can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise habits, stress levels, and underlying medical conditions. Treatment for high blood pressure may involve lifestyle changes, such as improving diet and exercise habits, or medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
In the end, managing high blood pressure means keeping a close eye on it and taking steps to prevent further health problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are important in detecting any early signs or symptoms of hypertension so that treatment options can be thoroughly explored. By making small changes in daily routine like eating healthier diets low in sodium content; engaging in regular physical activity; quitting smoking; limiting alcohol intake; reducing stress levels through meditation techniques among others – individuals diagnosed with HBP can take control over their health while living fulfilling lives free from chronic illness.
Prevalence and impact on health
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), high blood pressure is responsible for over 7 million deaths globally every year. It is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke and kidney failure.
The impact of high blood pressure on an individual’s health can be severe. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as heart attack or stroke. High blood pressure can also cause damage to important organs like the kidneys and eyes. In addition to physical health problems, high blood pressure can have a negative impact on mental health as well. The stress of managing the condition may lead to anxiety and depression.
Fortunately, there are ways to prevent and manage high blood pressure through lifestyle changes like exercise, healthy diet choices, and reducing salt intake. A doctor or nurse may also give you medicines like diuretics or ACE inhibitors if you need them. Early detection and management of high blood pressure are key in preventing long-term complications and improving overall health outcomes for those affected by it.
Importance of understanding HBP
High blood pressure (HBP) is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of arteries is too high and can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure if left untreated. Understanding HBP is crucial because it helps individuals take the necessary steps to prevent or manage the condition.
Knowing your blood pressure numbers and what they mean is an essential first step in understanding HBP. Blood pressure readings consist of two numbers: systolic (the top number) measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats, while diastolic (the bottom number) measures the pressure between beats. A normal blood pressure reading should be less than 120/80 mmHg.
Prevention plays a significant role in managing HBP. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, reducing salt intake, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption are all effective ways to control high blood pressure levels. In some cases, healthcare professionals may also give you medicine to help lower your blood pressure. Overall, understanding HBP enables individuals to make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps toward preventing or managing this potentially life-threatening condition.
II. Understanding High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Often referred to as “hypertension,” this condition occurs when the force of blood flowing through your arteries is consistently too high. This can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and vision loss.
There are several symptoms associated with high blood pressure, which include headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath and chest pain. However, in many cases, people with high blood pressure may not experience any noticeable symptoms at all. The best way to know if you have high blood pressure is by getting regular check-ups with your doctor.
To prevent or manage high blood pressure, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, reducing salt intake, and exercising regularly. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed by your doctor to help regulate your blood pressure levels. In order to keep your condition under control and lower the risk of complications, it’s crucial to adhere to any treatment plan that your healthcare provider advises.
Blood Pressure basics: Systolic and Diastolic
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure are two important measures of a person’s overall blood pressure. Systolic pressure is the top number in a blood pressure reading, and it represents the amount of pressure that is exerted on the walls of arteries when the heart beats. In contrast, diastolic blood pressure is the bottom number in a reading, and it represents the amount of pressure that is present in the arteries when the heart rests between beats.
When either one or both numbers are too high, this indicates hypertension (high blood pressure), which can increase your risk for serious health problems such as heart disease or stroke. Maintaining healthy levels of both systolic and diastolic blood pressure through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can help prevent hypertension. Also, if making changes to your lifestyle isn’t enough to control high blood pressure, you may be given medicine.
Overall, knowing what systolic and diastolic pressures mean can help keep your health in good shape. Keeping an eye on your blood pressure on a regular basis can also help you catch any problems before they become more serious.
Causes of HBP: genetics, lifestyle, underlying health conditions
High blood pressure (HBP) is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can lead to serious health problems such as stroke and heart disease if left untreated. HBP is caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions.
Genetics play a significant role in the development of HBP. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of hypertension are more likely to develop high blood pressure themselves. This may be due to inherited traits that affect the way our bodies regulate blood pressure.
Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to HBP. A diet high in sodium and saturated fats has been linked to an increased risk of developing hypertension. Inactivity and obesity are also known risk factors for HBP. Furthermore, smoking damages the walls of the arteries, which causes them to narrow, leading to an increase in blood pressure levels.
Finally, underlying health conditions like kidney disease, sleep apnea, or hormonal imbalances can also lead to high blood pressure. These conditions cause changes in the body’s systems that impact blood flow and regulation.
It is important to try to prevent or control high blood pressure by making changes to your lifestyle or taking medicine prescribed by a doctor based on your needs and medical history.
Risk factors for HBP: age, obesity, smoking, stress, family history, etc.
Age, obesity, smoking, stress, and family history are all known risk factors for high blood pressure (HBP). As individuals age, their chances of developing HBP increase. This is because the arteries tend to become stiffer and narrower with age, which can lead to a rise in blood pressure. Obesity is another significant risk factor for HBP, as excess body fat can lead to an increase in resistance within the blood vessels.
Smoking also contributes significantly to the development of HBP. Nicotine present in cigarettes raises blood pressure by narrowing the arteries and stimulating the release of adrenaline, which causes an increase in heart rate. Stress is another thing that can cause blood pressure to rise temporarily or stay high for a long time. It is important for individuals to find ways to manage stress levels, such as meditation or exercise.
Finally, having a family history of HBP puts one at greater risk of developing this condition themselves. It may be due to shared genetics or environmental factors that affect multiple members of a family. However, by making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and reducing stress levels through regular exercise or meditation, it is possible to mitigate these risks and reduce your chances of developing high blood pressure.
III. Signs and Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unfortunately, many individuals may not even realize they have the disease because it often presents with no symptoms. However, in some cases, high blood pressure can result in visible signs such as headaches or dizziness.
One common symptom of high blood pressure is nosebleeds. Even though nosebleeds aren’t always a sign of high blood pressure, they could be if they happen along with other symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Also, people with high blood pressure often have trouble seeing, like blurred vision or trouble focusing.
Other signs and symptoms of high blood pressure include fatigue and weakness. When your body has to work harder to pump blood throughout your system due to elevated pressures within arteries and vessels throughout the body, it can lead to feelings of lethargy and tiredness that don’t go away even after getting enough rest at night.
Overall, high blood pressure may not always show visible signs, but if you notice any of the above signs, you should take them seriously and see your doctor to find out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
Early signs and symptoms
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unfortunately, high blood pressure often goes undetected until it becomes a serious problem. However, there are some early signs and symptoms you can look out for to ensure you catch it before it gets too dangerous.
One of the most common early signs of high blood pressure is headaches. If you get headaches often or for a long time, especially around the temples, this could mean that your blood pressure is too high. Another symptom to be aware of is dizziness or lightheadedness when standing quickly from a sitting or lying position.
Other early warning signs of high blood pressure are shortness of breath during exercise or physical activity and chest pain (angina) caused by the heart muscle not getting enough oxygen. Additionally, if you notice any changes in your vision, such as blurred vision or seeing spots, this could also be a sign that your blood pressure is too high.
It’s important to keep in mind that these symptoms may not necessarily indicate high blood pressure on their own but rather serve as indicators for further investigation by a medical professional. Regular checkups with your doctor can help find any hidden problems and get them treated quickly, before they get worse.
Complications of untreated HBP: heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, etc.
Untreated high blood pressure (HBP) can lead to a plethora of complications that extend beyond just heart attacks and strokes. For instance, HBP can cause damage to the kidneys over time, which is why it is often referred to as the “silent killer.” HBP makes the blood vessels in the kidneys weaker and smaller if it is not treated, which can lead to kidney failure. This complication has become quite rampant in recent times because most people are not aware of their BP levels until they start experiencing symptoms.
Furthermore, untreated HBP can also cause vision problems such as blurred or impaired vision due to damage done to small blood vessels in the eyes over time. Additionally, it increases your chances of developing metabolic syndrome – an umbrella term used for conditions such as obesity and insulin resistance that increase your risk for diabetes and other diseases. The good news is that high blood pressure is easy to take care of if it is caught early and treated with medication or changes in lifestyle, like regular exercise and eating well.
In conclusion, neglecting a diagnosis of high blood pressure can have serious consequences for one’s health if left untreated. It’s important not only to get tested regularly but also to adopt preventative measures by monitoring sodium intake, maintaining a healthy weight range through regular physical activity, and addressing any symptoms promptly with medical intervention. By taking these steps today, you’ll be protecting yourself from some of the worst effects of this disease tomorrow!
IV. Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure
The diagnosis of high blood pressure is typically based on multiple readings taken over time. A single elevated reading does not necessarily mean that someone has high blood pressure. It is important to keep in mind that some people experience “white coat hypertension,” which means their blood pressure increases due to the stress of being in a doctor’s office. To confirm a diagnosis, doctors may recommend ambulatory monitoring or self-monitoring at home.
Ambulatory monitoring involves wearing a small device that measures your blood pressure every 30 minutes or so throughout the day and night. This can make the readings more accurate and help find patterns of high or low blood pressure. Self-monitoring at home involves using a special cuff and monitor to measure your own blood pressure several times per day for several days.
In addition to these methods, doctors may also perform additional tests to evaluate for any underlying conditions that could be contributing to high blood pressure, such as kidney disease or sleep apnea. Once you’ve been given a diagnosis, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to come up with an effective treatment plan.
Methods of diagnosis: office blood pressure measurement, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, home blood pressure monitoring
Office blood pressure measurement, also known as a clinic or in-office blood pressure monitoring, is a common method of diagnosing high blood pressure. A healthcare professional typically performs this by measuring the force of blood against the artery walls using a sphygmomanometer and an inflatable cuff placed around the upper arm. These readings can be influenced by factors such as anxiety or “white coat syndrome,” which may artificially elevate the results.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) involves wearing a small, portable device that checks your blood pressure at regular times during the day and night. The ABPM gives more accurate readings than office tests, so you can learn more about how your blood pressure changes over time. It can also help identify any underlying causes of high blood pressure, such as sleep apnea.
Home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) is another way to diagnose high blood pressure. This method involves using a personal, home-use device to measure your own blood pressure at different times throughout the day for several days or weeks. HBPM allows you to take measurements in comfortable settings without external stimuli that can interfere with the accuracy levels observed during clinical procedures. The ability to track changes in blood pressure in different places gives patients a chance to take an active role in managing their care and improving their health through self-monitoring and early detection.
Classification of HBP: normal, prehypertension, stage 1 and stage 2 hypertension
High blood pressure (HBP) is a common health problem that affects millions of people worldwide. HBP is classified into four categories based on the severity of the condition, which include normal, prehypertension, stage 1, and stage 2 hypertension.
The first category is normal blood pressure, where systolic blood pressure (SBP) is less than 120 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) is less than 80 mmHg. Prehypertension refers to SBP between 120 and 139 mmHg or DBP between 80 and 89 mmHg. Stage 1 hypertension occurs when SBP ranges from 140–159 mmHg or DBP ranges from 90–99 mmHg.
Stage 2 hypertension has an SBP greater than or equal to 160 mm Hg and a DBB greater than or equal to 100 mm Hg. These categories are important because they help doctors and nurses figure out the best way to treat their patients.
In the end, knowing how high blood pressure is classified can help people understand their risk factors and take steps to prevent or treat it. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and reducing stress levels can also contribute to maintaining normal blood pressure levels in individuals with prehypertension or the early stages of hypertension.
Importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring
Accurate diagnosis and monitoring are essential when it comes to treating high blood pressure. While some may have clear symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, or shortness of breath, others may not exhibit any visible signs. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect high blood pressure at an early stage, thus making it easier to manage the condition.
Once diagnosed, monitoring becomes crucial in determining if the prescribed medications are working effectively. If left untreated or not monitored properly, high blood pressure can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, or kidney damage. Therefore, patients must keep track of their blood pressure readings and follow up with their healthcare providers regularly.
In conclusion, accurate diagnosis and monitoring play a vital role in managing high blood pressure effectively. Patients should see a doctor right away if they have symptoms of high blood pressure, and they should keep getting regular checkups even after they have been given medication. This will make sure that any changes in the patient’s condition are caught early so that the right steps can be taken before they cause serious problems.
V. Treatment and Management of High Blood Pressure
One of the primary treatment options for high blood pressure is medication. There are several types of medications available, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers. The choice of medication will depend on various factors, such as the patient’s age, overall health status, and other medical conditions they might have.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can also help manage high blood pressure. Among these are keeping a healthy weight by working out regularly and eating a balanced diet that is Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to make any needed changes to their treatment plan. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to make any needed changes to their treatment plan. People with high blood pressure can live healthy lives without the problems that come with the condition if they take care of it and change how they live.
Lifestyle changes: diet, exercise, weight loss, smoking cessation, stress management
Diet plays a crucial role in managing high blood pressure. A diet that is low in sodium, fat, and cholesterol and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate blood pressure levels. Additionally, reducing the intake of processed foods can also help lower blood pressure. It’s also a good idea to limit how much alcohol you drink, since drinking too much can raise your blood pressure.
Regular exercise is another key lifestyle change that can help manage high blood pressure. Aerobic exercises such as brisk walking or cycling for at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week, can help lower blood pressure levels. Resistance training exercises such as weightlifting or push-ups are also beneficial for those with high blood pressure.
People with high blood pressure must stop smoking because it raises both their heart rate and blood pressure. If you stop smoking for good, you may not only lower your blood pressure, but you may also lower your risk of other health problems that are linked to smoking.
Lastly, stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga have been shown to reduce stress levels, which ultimately lower overall hypertension rates among individuals practicing these relaxation techniques regularly.
Medications for HBP: types, side effects, adherence, monitoring
There are several types of medications that may be prescribed for hypertension, also known as high blood pressure (HBP). These include diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin II receptor blockers. Each type works differently to lower blood pressure and may have different side effects.
Common side effects of HBP medications include dizziness, headaches, fatigue, decreased libido, and a dry mouth. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about any possible side effects and to report any problems right away. Adherence to medication schedules is another important aspect of managing HBP. To keep their blood pressure under control, patients should take their medications as their doctor tells them to.
Monitoring blood pressure levels regularly is essential when taking HBP medication. This gives doctors the ability to change dosages or switch medicines as needed to get the best control of blood pressure. Patients can also monitor their own blood pressure at home using a personal monitor and share the results with their healthcare provider for further management guidance.
Complementary and alternative therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies are becoming increasingly popular to manage high blood pressure. Instead of just using medicine, these treatments focus on using natural remedies and techniques to lower blood pressure. Some of the most popular complementary therapies include acupuncture, yoga, meditation, and aromatherapy.
In acupuncture, tiny needles are put into certain points on the body to increase the flow of energy and help lower blood pressure. Yoga is a gentle form of exercise that can help reduce stress and anxiety, which are known contributors to high blood pressure. Meditation is also a good way to deal with stress and help you relax, which can help your blood pressure in the long run. Aromatherapy uses plant oils like lavender or chamomile that have been shown to calm the body.
Even though these alternative therapies might not be able to take the place of traditional medications prescribed by a doctor to treat high blood pressure, they can be used together with those medications to get better results. It’s important to discuss any complementary or alternative therapies with your healthcare provider before starting them, as they may interact with current medications or have unintended side effects.
VI. Prevention of High Blood Pressure
Preventing high blood pressure is much easier than curing it. Simple lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing high blood pressure. High blood pressure can be prevented in a very effective way by keeping a healthy weight, working out regularly, and eating less salt. It’s also recommended to limit alcohol consumption and quit smoking.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help prevent high blood pressure. Foods that are high in potassium, such as bananas, avocados, spinach, and sweet potatoes, have been found to be beneficial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Adding stress-relieving activities like yoga or meditation to your daily routine can also help keep your blood pressure in a healthy range.
In summary, making small lifestyle changes like eating a healthier diet with less salt intake and more potassium-rich foods while maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can effectively prevent the development of high blood pressure. Limiting the amount of alcohol you drink and giving up smoking, along with stress-relieving activities like yoga or meditation, will lower your chances of getting high blood pressure even more.
Primary prevention: healthy lifestyle choices, regular check-ups
High blood pressure can be prevented in the first place by making healthy choices and going to the doctor regularly. Hypertension can be avoided by staying at a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in sodium, and getting regular exercise. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also important factors to consider.
Regular checkups with a doctor or nurse can help people keep an eye on their blood pressure and spot any problems early on. Blood pressure screenings are typically done during routine medical exams or as part of preventative health screenings. Individuals should aim to have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years, but more frequent checks may be necessary depending on individual risk factors.
Overall, taking steps towards a healthy lifestyle and staying up-to-date with regular check-ups can significantly reduce the risk of developing high blood pressure. By putting first-line prevention measures like these at the top of their list, people can take charge of their health and possibly avoid long-term problems caused by high blood pressure.
Secondary prevention: early diagnosis and treatment, medication adherence, regular monitoring
Secondary prevention plays a crucial role in managing high blood pressure (HBP). Early diagnosis and treatment of HBP can help prevent complications such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. To make sure that medicine is working, it is important to check blood pressure levels regularly. Patients should work closely with their doctor to make a personalized treatment plan that includes changes to their lifestyle and taking their medications as prescribed.
Medication adherence is critical in the management of HBP. For the best results, patients must take their medicine exactly as their doctor tells them to. If you skip doses or stop taking your medicine altogether, your blood pressure may get out of control and you may be more likely to have problems. Healthcare providers may use reminder systems or simplified dosing schedules, among other things, to help patients follow their treatment plans.
Patients with high blood pressure (HBP) need to be checked regularly to see how well their treatment is working, to keep an eye on any possible side effects, and to make any necessary changes to their medications. Patients should track their blood pressure readings at home using an electronic or manual monitor and share them with their healthcare provider during regular check-ups. This information helps doctors and nurses make better decisions about how to care for their patients and gives patients more power over how their health turns out.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, high blood pressure is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is often called the “silent killer” because it has no visible symptoms and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. But you can easily avoid or control this condition if you get regular checkups and keep an eye on your blood pressure getting better or worse.
One way to prevent high blood pressure is by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes getting regular exercise, eating less salt, giving up smoking, and drinking less alcohol. In some cases, a doctor or nurse may also give you medicine to help control your blood pressure.
It’s important to remember that dealing with high blood pressure requires a long-term commitment to living a healthy life. By keeping an eye on your health and taking steps to prevent or control high blood pressure, you can lower your chances of developing serious health problems that are linked to this condition.